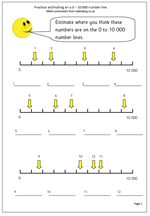
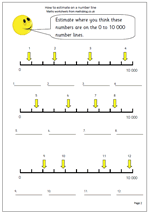
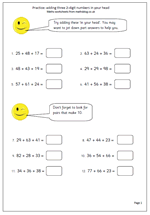
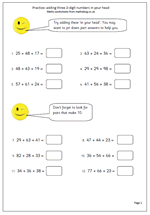
Many children in Year 6 have difficulty reading and writing large numbers, including millions. This page is all based on millions as it looks at the area in square kilometres of some of the largest countries in the world. The task is to round the numbers to the nearest million, and as it happens all of these need to be rounded down.
It is well worth ‘talking through’ this page to make sure that the numbers are read correctly.