There are times and dates, interesting times and dates and really incredibly fantastic times and dates and the good news is that we are rapidly approaching one of the all time best. You will probably not live long enough to beat this!
On the eleventh second of the eleventh minute of the eleventh hour of the eleventh month 2011 the date will be 11.11.11.11.11.
Wow!
There are plenty of myths flying around that something incredibly good, or something incredibly bad is going to happen, with cosmic shifts and all sorts, but I believe that there is no scientific evidence for any such thing and that nothing out of the usual will happen. Or I could be wrong! Nevertheless, it is a great date to remember and those of you who have followed this blog over the years will know that I really like the patterns these dates make.
Of course the eleventh of the eleventh is well known as the anniversary of the end of the first world war, with two minute silences held at 11 am on Remembrance Sunday.
A new movie, called, you guessed it, 11.11.11 should be released on this day.
Also quite peculiar is this little fact;
Take the last two digits of your year of birth, plus the age you will be this year. Add them together and it will be…….111!
In the binary system the number 1111111111 has a value of 1023 in the decimal system (512 + 256 +128 + 64 + 32 + 16 + 8 + 4 + 2 + 1)
Plenty of interesting patterns to explore there!
Whilst we are looking at 111…. why not have a look at this fantastic prime number:
1111111111 1111111111 1111111111 1111111111 1111111111 1111111111
1111111111 1111111111 1111111111 1111111111 1111111111 1111111111
1111111111 1111111111 1111111111 1111111111 1111111111 1111111111
1111111111 1111111111 1111111111 1111111111 1111111111 1111111111
1111111111 1111111111 1111111111 1111111111 1111111111 1111111111
1111111111
1111111 (317 digits)
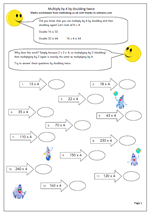
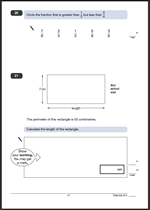
 I have published worksheets on ordering decimals before, but this page, lent to me from urbrainy.com is a very neat way of making sure that decimals are put in order correctly.
I have published worksheets on ordering decimals before, but this page, lent to me from urbrainy.com is a very neat way of making sure that decimals are put in order correctly.