By year 4 children should be confident enough to count on in steps of 50 or 25. This can be useful when using money or length. Here we have a straightforward free maths worksheet that looks at counting in these steps. Some of the counting on in fifties start with multiples of 50 but the later questions don’t, but children should quickly see the patterns involved.
Coming soon: counting, calculator game and dividing decimals
 A mixed bag of activities coming next week.
A mixed bag of activities coming next week.
By year 4 children should be confident enough to count on in steps of 50 or 25 and we will be publishing a practice sheet on this as it is seldom found elsewhere, but does come into the Year 4 objectives.
We will also be publishing another in our series of using a calculator to help learn and reinforce tables. To be successful with this game you need to know your 5x table: the calculator just confirms your correct mental arithmetic (or not!). Suitable for Year 3 upwards.
Also coming soon is a good revision sheet for Year 6 to make sure that they understand the process of dividing decimals by 10 or 100. Knowledge of this is crucial for success in High School.
Maths worksheet: Multiply decimals
There are some definite dos and don’ts when it comes to multiplying decimals ‘in your head’.
To multiply by 10 move each digit one place to the left, including tenths to the units, if necessary.
To multiply by 100 move each digit two places to the right.
The big don’t is to think that ‘add a nought’ is a short cut to multiplying by 10. 2.3 x 10 is not 2.30!!
This is a good check up page to make sure children understand what they are doing.
Resource of the week: Tables square and square numbers
This worksheet has a 10×10 multiplication square which is a brilliant aid to helping with tables, but it is also excellent for showing the pattern of square numbers from 1 to 10.
A square number is made by multiplying a whole number by itself. eg 4 x 4 = 16.
16 is a square number.
It is quite useful to learn the first 10 square numbers off by heart:
1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100.
We will look more closely at square numbers later.
Resource of the week: Equivalent fractions
Once the idea of equivalent fractions has been understood it becomes possible to compare two fractions to see which is the larger. The first thing to remember is that the larger the number on the bottom of the fraction, the smaller each part of the fraction is. So 4/100 is much smaller than 4/25.
Now this is also easy if the bottom number (denominator) is the same in each fraction eg 1/5 is smaller than 3/5.
The difficulty comes when the numbers are not the same. How do you compare 3/5 with 7/10?
The easiest way is to make the bottom number of each fraction the same, and in the case above this will mean converting the 3/5 into tenths. We can do this by multiplying the 5 by 2 to make 10 and we have to do the same with the top number, multiplying the 3 by 2. In this way 3/5 can be converted to 6/10.
3/5 and 6/10 are equal, or equivalent.
It is now easy to see that 6/10 is smaller than 7/10, so 3/5 must also be smaller than 7/10. Job done!
Later it will become harder to convert so that the denominators are the same; sometimes you have to multiply both fractions by different numbers, but this comes later! At the moment it is important to get the basics correct.
Maths worksheet: Subtraction of money
Using written methods of subtraction can prove quite tricky with money as it involves decimals. It is important to lay the question out in the standard way, even if it is shown horizontally or just as a written problem and most importantly, to keep the decimal points in a line.
Watch out when there is a zero on the top line as many children go for the easy option and say ‘nought take away 3 is 3’ rather than going through the carrying process.
This is the second in our series on subtracting money.
Counting back in tens: Year 3 revision
In year 3 many children still find it tricky to count on and back and there is a danger that they are moved on to harder maths before they have mastered this basic skill. This is a page which can be used as a check to make sure that they are confident with counting back in tens from any 2 or 3-digit number.
Free maths resources: a number week
 Next week our free maths resources are very much to do with counting and number.
Next week our free maths resources are very much to do with counting and number.
Firstly we have a page on revising counting back in whole tens from any 2-digit or 3-digit number. Some children still find this difficult in Year 3, especially when it involves crossing a hundreds boundary. If children do find this hard it is well worthwhile going back to a large number square and making sure that they are confident with counting on, crossing the hundreds boundary.
We also have something harder for those who are getting to grips with written methods of subtraction. Using written methods of subtraction can prove quite tricky with money as it involves decimals. It is important to lay the question out in the standard way, even if it is shown horizontally or just as a written problem and most importantly, to keep the decimal points in a line.
We also have another page on multiplying mentally. There are some definite dos and don’ts when it comes to multiplying decimals ‘in your head’, which Year 6 children should be well aware of as they approach going on to High School.
To multiply by 10 move each digit one place to the left, including tenths to the units, if necessary.
To multiply by 100 move each digit two places to the right.
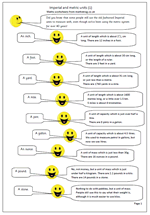
Year 6 maths worksheet: Imperial and metric units
It is a sad state of affairs that schools are still having to teach children to convert imperial to metric units, even when we have been metric for over 40 years. Many adults still use feet and inches to measure their height, use miles per gallon in their cars and stones and pounds to measure their weight. Yet a great many do not know how many pounds there are in a stone or how many yards there are in a mile, making the whole thing nonsensical and bewildering to children.
Nevertheless, here it is, a page of conversions with some info about the imperial system.
Convert imperial to metric units (1)
Resource of the week: relate division and fractions
Something in the archives for Year 5 this week. The relationship between fractions and division is one which many children fail to grasp. Put simply, one fifth of 30 is equivalent to 30 divided by 5, or written as a fraction 30 over 5.
It can be a great help to see a fraction as a division calculation. 1/2 can also be thought of as one divided by two.
This page takes a quick look at this and should show whether your child does understand this important relationship.